GPCI-Startup Ecosystems
As evaluation factors for the startup field, 21 indicators grouped into 5 categories were selected. Each indicator was scored and averaged to calculate the score for each indicator group, which were then combined to derive the overall score for the startup function. In the startup functions rankings, San Francisco was redefined as the broader metropolitan area of “Silicon Valley.” As a result, the analysis covered 47 cities from the GPCI list, excluding San Francisco, plus 1 area (Silicon Valley).The overall ranking for GPCI-Startup Ecosystems was created by adding the startup function scores to the scores from the six functions of the GPCI.
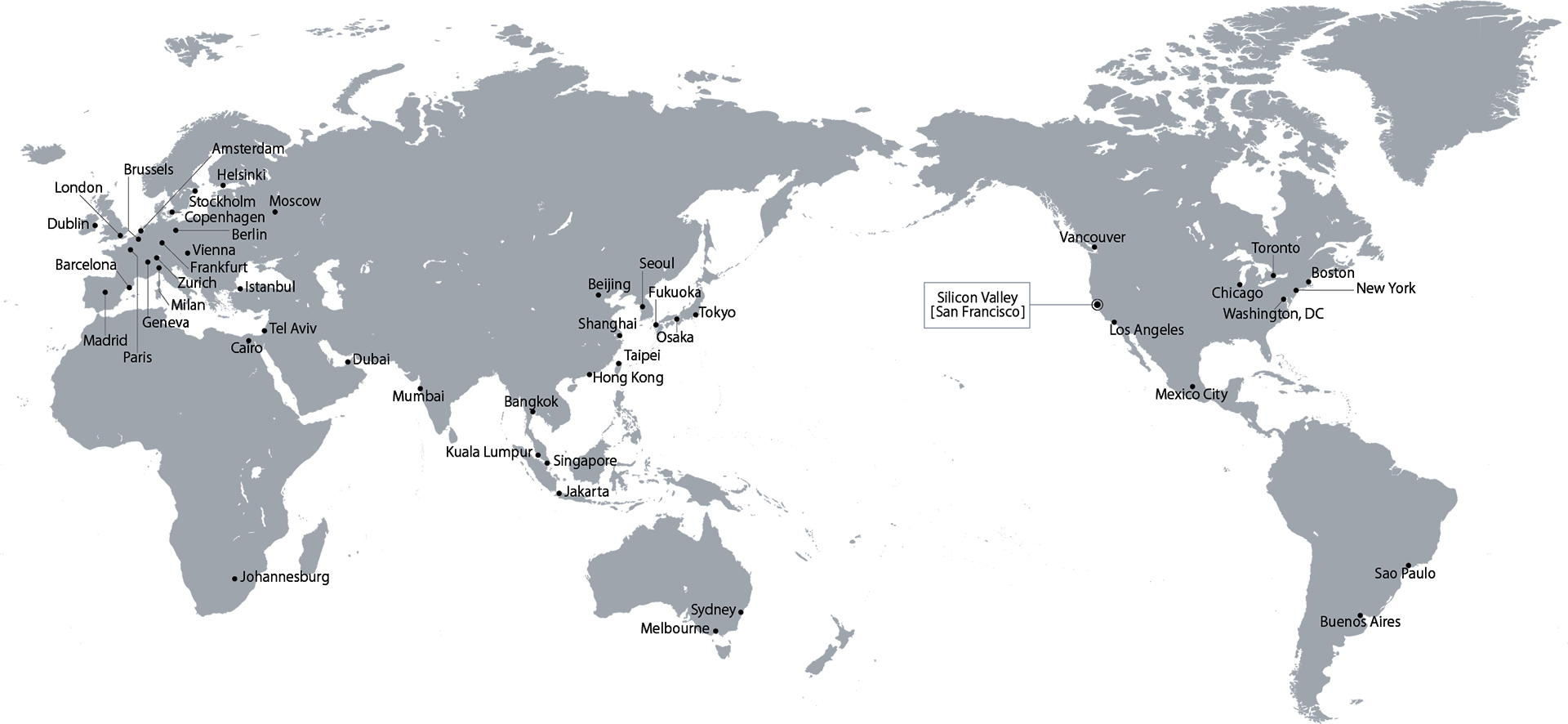
Target Cities
In the startup field rankings, an exception was made for San Francisco, redefining it as the broader metropolitan area of “Silicon Valley.” As a result, the analysis covers 47 cities from the GPCI list, excluding San Francisco, plus 1 area (Silicon Valley). Silicon Valley, with its mature ecosystem that hosts leading global tech companies, educational and research institutions, and investors, serves as a benchmark for the competitiveness of the 47 cities included in the GPCI.
Executive Summary
Startup Function Ranking
Comprehensive Ranking (GPCI-2025 + Startup Function)
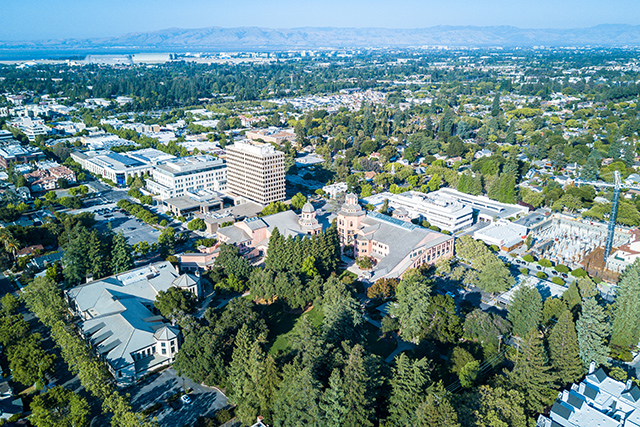

Silicon Valley, which secured the top position in the startup function, also ranked first across all indicator groups except for “Entrepreneurial Talent & Education Environment”. In particular, it achieved first place in every component indicator within both “Entrepreneurship Dynamism” and “Scale-up Dynamism”. Moreover, it led in Number of Accelerators & Incubators and Wage Level under the “Entrepreneurial Environment” group, as well as in Scale-up Talent Mobility under the “Scale-up Environment” group. Even as a standalone city, San Francisco demonstrates top-tier competitiveness among the 48 GPCI cities. When assessed together with the surrounding counties as Silicon Valley, its performance across all indicator groups is further reinforced, underscoring its overwhelming global competitiveness.
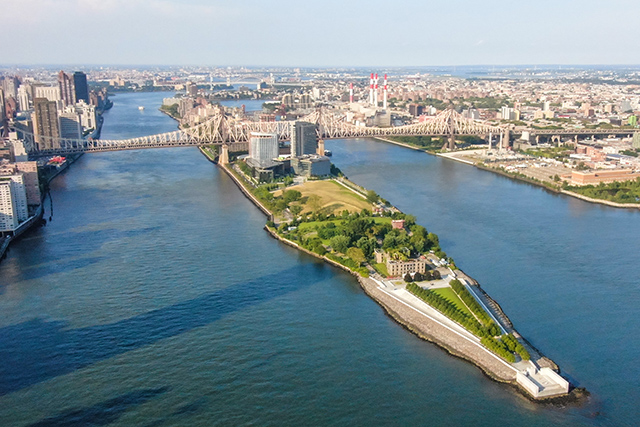

New York, which ranked second in Startup function, placed second in both “Entrepreneurial Dynamism” and “Scale-up Dynamism”, following Silicon Valley, and third in “Entrepreneurial Environment” and “Scale-up Environment”. Among its strengths is ICT Readiness, a category in which all major American cities perform strongly. In addition, it ranked second to Silicon Valley in several other key indicators, including Early-stage Funding Size, Number of Early-stage Investors, Scale-up Talent Mobility, Mid & Late-stage Funding Size, Number of Mid & Late-stage Investors, and Number of Unicorns. Furthermore, New York secured third place in Startup Job Market and Number of Founders Originating from Top Universities, reflecting the city’s active talent and capital flows.
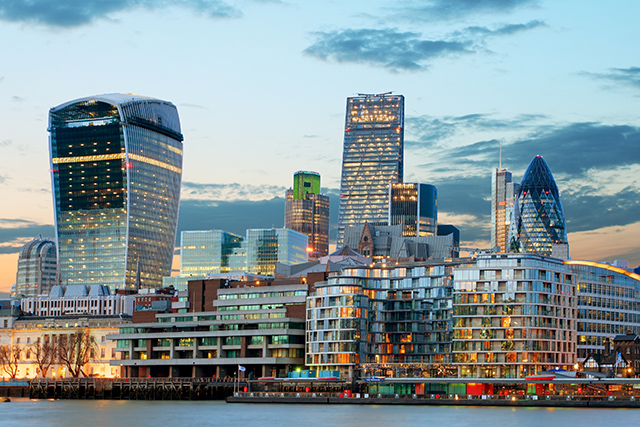

London, which ranked third overall, demonstrated strong performance by securing second place in both “Entrepreneurial Environment” and “Scale-up Environment”, following Silicon Valley. It also ranked third in “Entrepreneurial Talent & Education Environment”, “Entrepreneurial Dynamism” and “Scale-up Dynamism”, highlighting its balanced strength. In terms of individual indicators, London ranked first in World’s Top Universities, Variety of Workplace Options, and Number of Startup Events. It also achieved second place behind Silicon Valley in Number of Accelerators & Incubators, Number of Startups, and Exit Size. Additionally, four other indicators placed third, demonstrating that, like New York, London has a high number of top-level indicators.
Contact
If you have any questions about the GPCI-2025 Startup Ecosystems, please contact iusall@mori-m-foundation.or.jp