This summary includes the background & objective, the evaluation methodology of the study, the data tables, and the 2018 results & analysis. The results & analysis features radar charts of specific cities and a cluster analysis of all target cities.
The in-depth report of this study is published in “Japan Power Cities Databook 2018” (Japanese only).
While the world's population is predicted to keep on growing in the years ahead, the population of Japan is expected to shrink rapidly as a result of a declining birth rate and an aging society. In facing such circumstances head on, cities across Japan, in order to maintain their dynamism, must harness their respective characteristics and push ahead with urban development, while maintaining the “magnetism” required to attract people and companies, as well as the “growth potential” that continually demonstrates their urban appeal and strengths. In the “Japan Power Cities–Profiling Urban Attractiveness”, a comparative and multi-faceted analysis of the strengths of the major cities of Japan was conducted to shed light on city characteristics such as strengths and attractiveness in the hope of contributing to the formulation and execution of an urban strategy plan.
Key Features
- 1Analyzing city characteristics based on 6 functions, 26 indicator groups and 83 indicators
- 2Visualizing city strengths and attractiveness by using radar charts
- 3Featuring quantitative data of each city for the purpose of formulating and executing an urban strategy plan
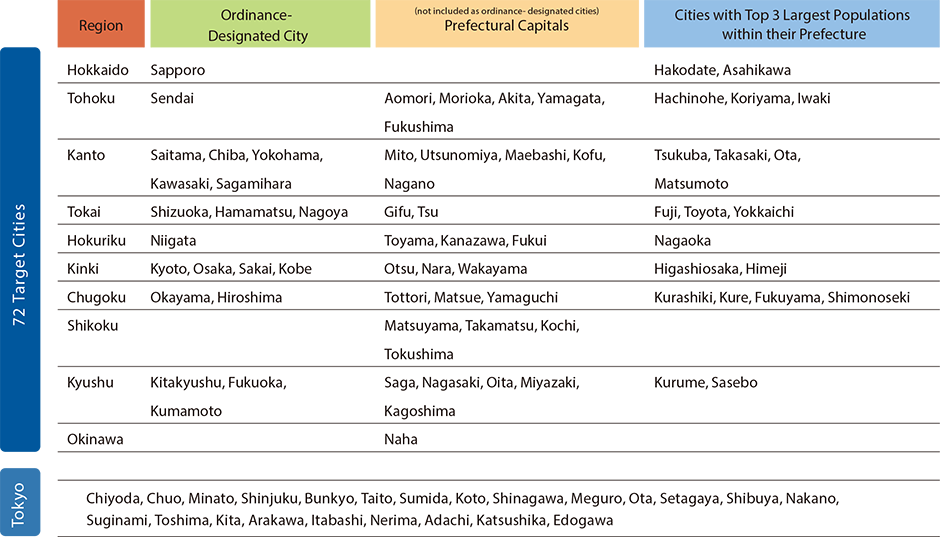
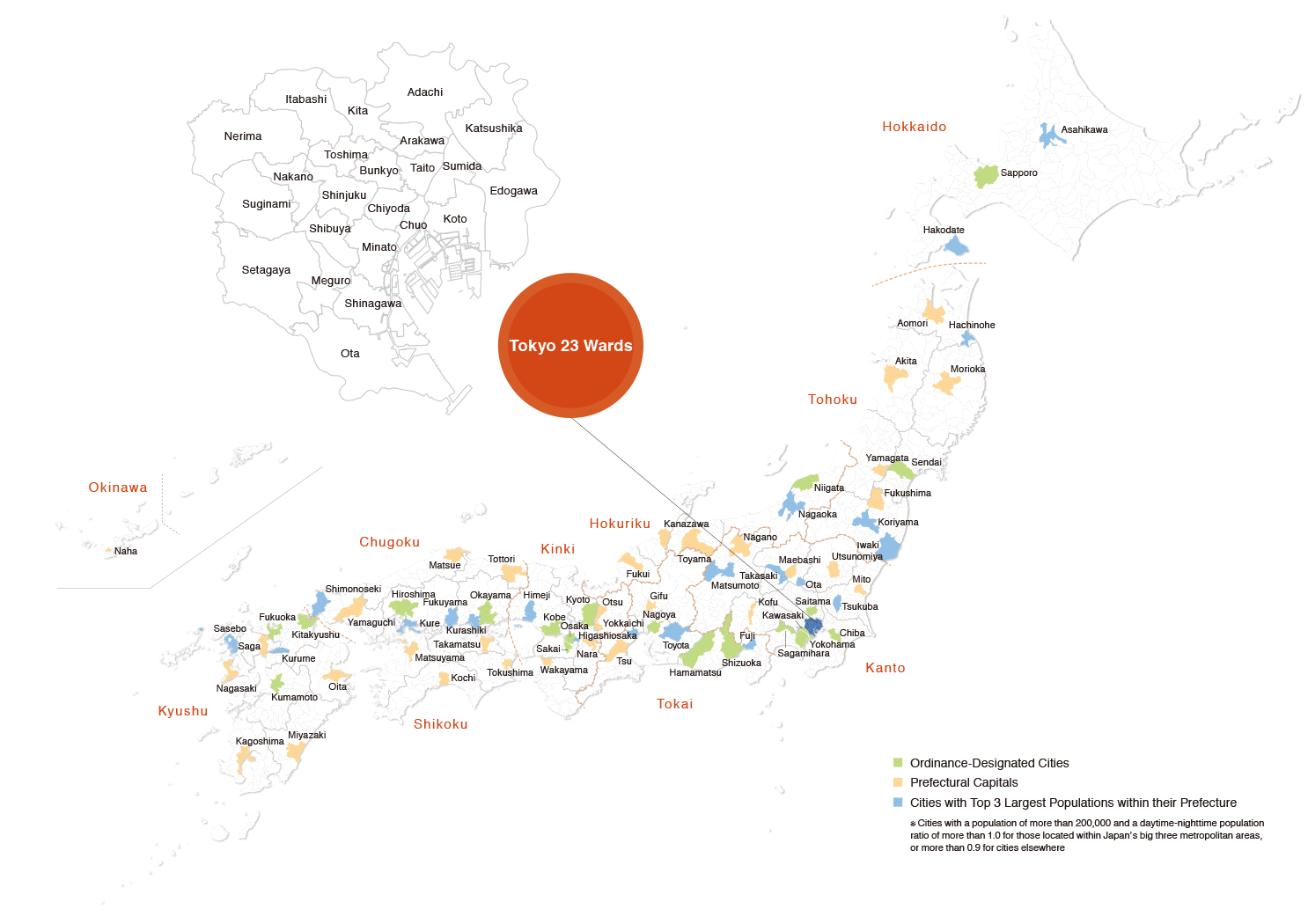
Target Cities
72 major Japanese cities and the 23 wards of Tokyo were included as target cities in this study. The 72 major cities comprise those designated by government ordinance, prefectural capitals, and the three biggest cities by population in each prefecture (cities with a population of more than 200,000 and a daytime-nighttime population ratio of more than 1.0 for those located within Japan's big three metropolitan areas, or more than 0.9 for cities elsewhere).
Evaluation Methodology
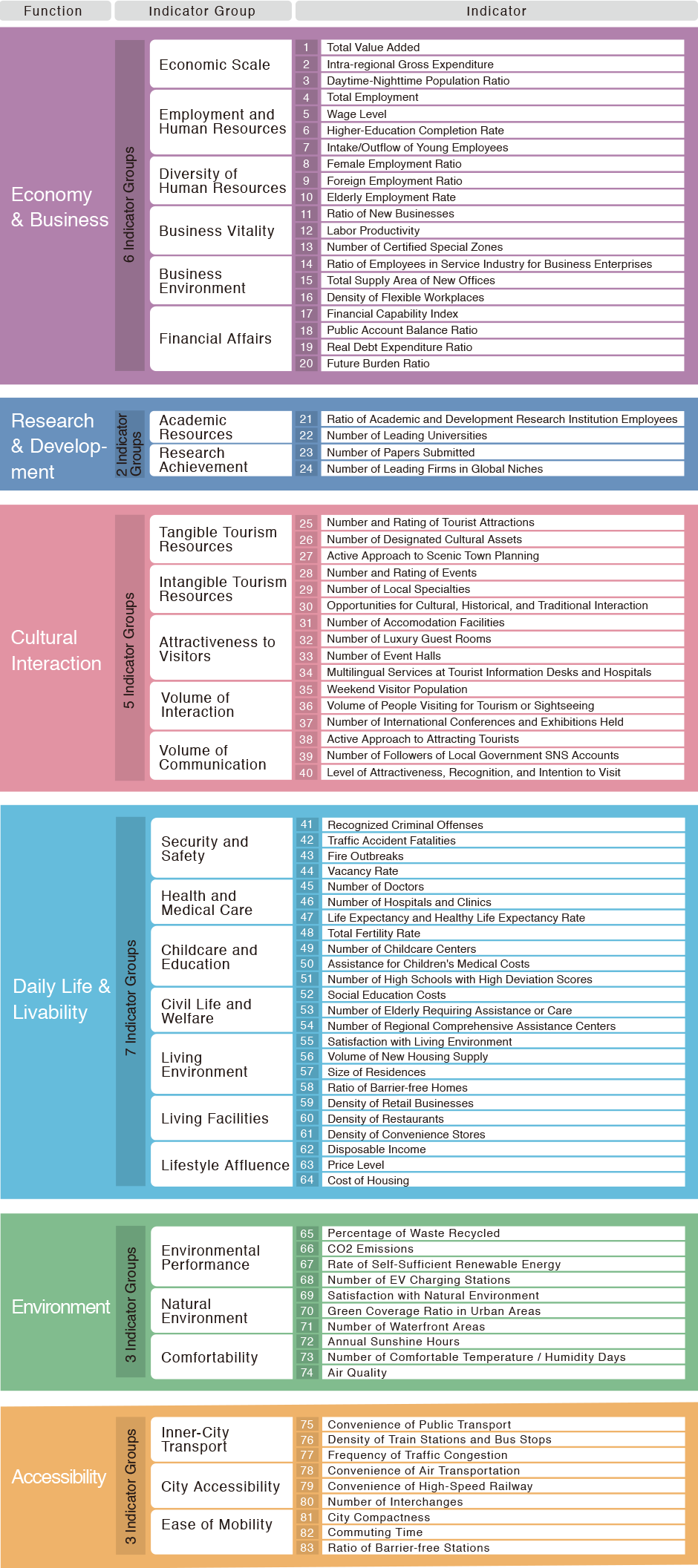
In this study, 6 functions (Economy & Business, Research & Development, Cultural Interaction, Daily Life and Livability, Environment, and Accessibility) were created to represent the components of cities. Furthermore, 26 indicator groups were established to represent the primary components of those functions, with 83 indicators finally being determined.
Function / Indicator Group / Indicator
Results
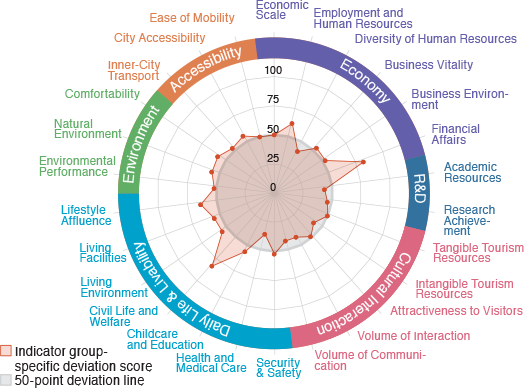
Radar charts and bar graphs were used to clarify the strengths and attractiveness of each target city in this study. The following are the examples of particularly unique cities, six of which are from a 72 major Japanese cities and three from the 23 wards of Tokyo.
72 major cities: Unique city example
Toyota
A financially stable company town
Tsukuba
A hub city of world-renowned research institutes
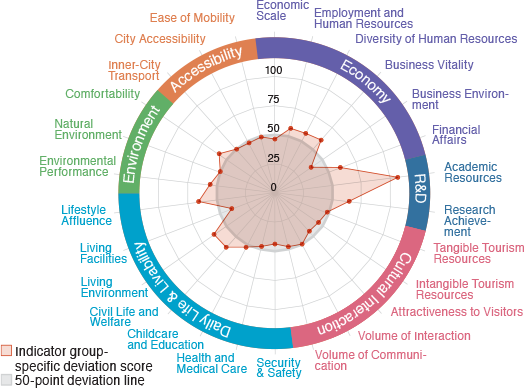
Sapporo
A tourist city full of soft cultural resources
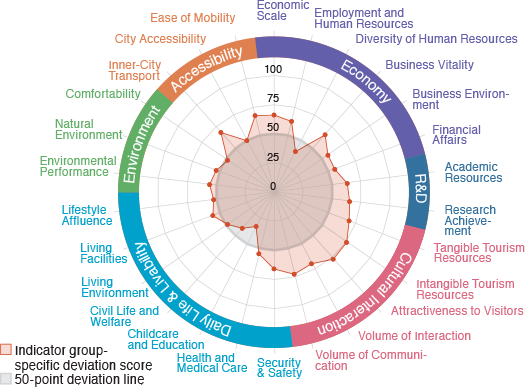
Fukui
A highly evaluated city in livability
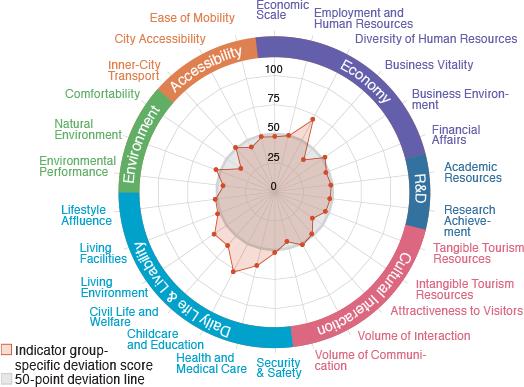
Matsue
A city full of natural environment
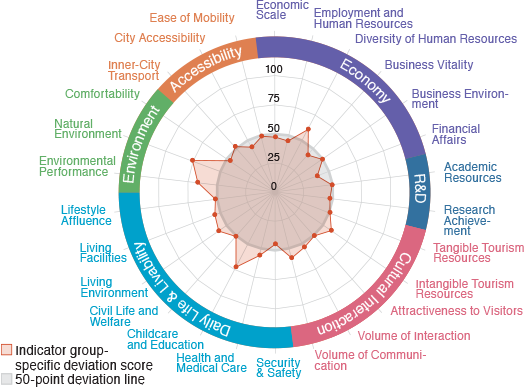
Naha
A compact city blessed with mild climate
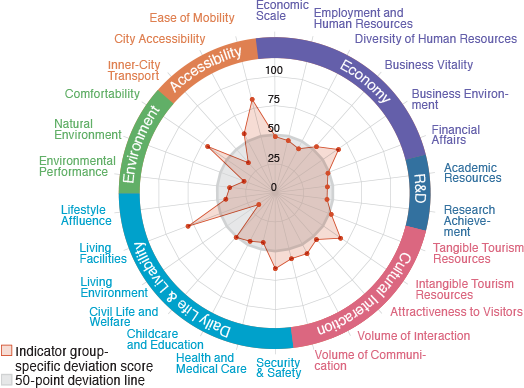
23 wards of Tokyo
Edogawa
A city with high satisfaction for its natural environment
and waterfront areas
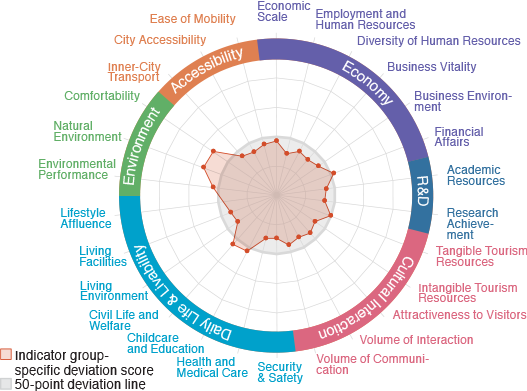
Minato
An international city with economic vitality
and cultural attractiveness
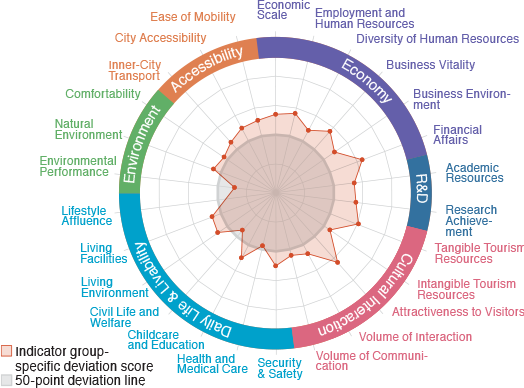
Bunkyo
A city outstanding in R&D and livability
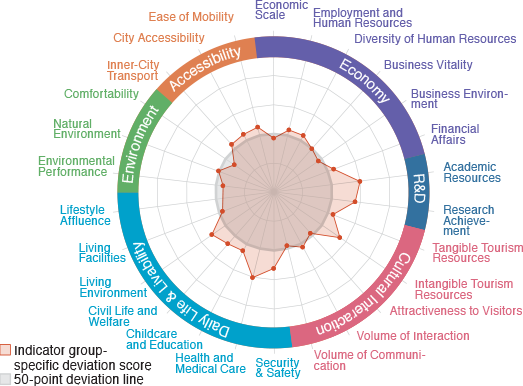
In the Databook 2018, you can find a city's characteristics
through different data forms including indicator group-specific radar charts.
Japan Power Cities Databook 2018
City characteristics of 72 major cities of Japan and 23 wards of Tokyo are revealed!
- Release date
- Print Edition: November 30th, 2018
PDF: November 20th, 2018 - Size
- A4/ 343 pages
- Language
- Japanese only
- Price
- Print Edition: JPY 32,400 (tax included)
PDF: JPY 25,920 (tax included) - Contents
- Introduction
Methodology
Results & Analysis
City Profiles
Data Tables
Reference
PUBLICATIONS
The Japan Power Cities (JPC) Databook profiles the strengths and special characteristics of major target cities located in Japan's administrative divisions, offering a multifaceted comparative analysis.
